Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
横山 須美*; 立崎 英夫*; 谷村 嘉彦; 吉富 寛; 平尾 茂一*; 青木 克憲; 立木 秀一*; 江崎 巌*; 星 勝也; 辻村 憲雄
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(3), p.031504_1 - 031504_17, 2022/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:31.61(Environmental Sciences)日本では、2021年4月に水晶体の等価線量限度が改定された。その結果、眼の水晶体の線量限度と実効線量の線量限度が等しくなった。放射線作業者,放射線安全管理者,免許取得者は、放射線防護に関連する規制を遵守し、防護を最適化する必要がある。日本保健物理学会が新たに開発した水晶体の線量モニタリングガイドラインでは、水晶体の線量が管理基準に近づいたり超えたりした場合、正確な推定のために目の近くで線量を測定することを推奨している。しかし、原子力発電所従事者の不均一な被ばくに関する情報は限られている。本研究では、日本の4つの商業用原子力発電所(RWR: 3基,BWR: 3基)において、高線量率作業場の線量当量および88名の作業員の個人線量を測定し、作業員の不均一な被ばくを分析した。
横山 須美*; 岩井 敏*; 辻村 憲雄; 橋本 周; 吉富 寛; 加藤 昌弘*; 黒澤 忠弘*; 立崎 英夫*; 関口 寛*; 小口 靖弘*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-15) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/00
In Japan, new regulations that revise the eye lens dose limit, operational quantities, and measurement positions for the dose of the lens will be enforced from April 2021. Based on the International and national guidelines, the results of the Radiation Safety Research Promotion Fund of Nuclear Regulatory Authority (NRA), and other studies, the Working Group of Radiation Protection Standardization Committee, the Japan Health Physics Society (JHPS), developed the guideline on the radiation monitoring for the lens of the eye. In July 2020, the guideline was published by the JHPS. The guideline consists of five parts: a main text, explanations, references, three attachments, and twenty-six questions. In the questions, the corresponding answers were prepared, and specific examples were given so that similar issues could be dealt with. In the working group, in particular, time was spent discussing judgment of the criteria of non-uniform exposure and the management criteria set to not exceed the dose limit to the lens. With the development of the guidelines on the radiation monitoring of the lens of the eye, the radiation managers and workers will be able to smoothly comply with revised regulations and optimize radiation protection.
 Am and
Am and  Sr/
Sr/ Y sources in terms of the eye lens monitoring in the nuclear facilities
Y sources in terms of the eye lens monitoring in the nuclear facilities吉富 寛; 古渡 意彦
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 188(2), p.191 - 198, 2020/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:24.28(Environmental Sciences)This paper highlights the issues of exposure inhomogeneity that are relative to eye lens monitoring for low-energy photons from  Am and beta-rays from
Am and beta-rays from  Sr/
Sr/ Y including a personal protective equipment because eye lens exposure has been concerned more than before due to the proposed reduction of relevant dose limit. These nuclides are common sources in the nuclear industry, which are particularly of concern. Our previous study presented a quantitative estimation of exposure inhomogeneity, which was applied to simple but typical exposure situations to the radionuclides. For the present study, exposure inhomogeneity of
Y including a personal protective equipment because eye lens exposure has been concerned more than before due to the proposed reduction of relevant dose limit. These nuclides are common sources in the nuclear industry, which are particularly of concern. Our previous study presented a quantitative estimation of exposure inhomogeneity, which was applied to simple but typical exposure situations to the radionuclides. For the present study, exposure inhomogeneity of  Am was approximately within a factor of 1.6, implying a rather homogeneous situation than expected. Regarding
Am was approximately within a factor of 1.6, implying a rather homogeneous situation than expected. Regarding  Sr/
Sr/ Y exposure, estimation from both
Y exposure, estimation from both 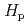 (10) and
(10) and 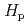 (0.07) on trunk would lead to an over- or underestimation by a factor of more than ten. In contrast,
(0.07) on trunk would lead to an over- or underestimation by a factor of more than ten. In contrast, 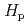 (3) measurement on trunk will improve by up to a factor of two. With respect to the personal protective equipment, lead apron and protective glasses are effective for the 60-keV photons for both anterior-posterior (AP) and rotational (ROT) irradiations, while a full-face respirator can reduce the eye lens dose by approximately 17% for
(3) measurement on trunk will improve by up to a factor of two. With respect to the personal protective equipment, lead apron and protective glasses are effective for the 60-keV photons for both anterior-posterior (AP) and rotational (ROT) irradiations, while a full-face respirator can reduce the eye lens dose by approximately 17% for  Sr/
Sr/ Y betas. As a whole, this study demonstrated that the effect of protective equipment can be effectively incorporated into the homogeneity evaluation.
Y betas. As a whole, this study demonstrated that the effect of protective equipment can be effectively incorporated into the homogeneity evaluation.
吉富 寛; 古渡 意彦; 萩原 雅之*; 長畔 誠司*; 中村 一*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 184(2), p.179 - 188, 2019/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:21.58(Environmental Sciences)To manage the equivalent doses for radiation workers, exposure inhomogeneity is an important factor in the decision-making process related to protection measures and additional monitoring. Our previous study proposed the methodology to evaluate the inhomogeneity of exposure quantitatively. In this study, we applied proposed method to five different types of actual exposure situations in the nuclear industry. Two of them were conventionally characterized as homogeneous exposure, but the other three as inhomogeneous exposure. The evaluation of homogeneity exposure was conducted using Monte Carlo calculations with two simplified models, which were then verified with phantom experiments. Consequently, all of the evaluations reproduced the experimental results, implying that our proposed method would be applicable for actual work conditions in the nuclear industry. Furthermore, the two presumed homogeneous exposure situations were found to be rather inhomogeneous because of the contribution of positrons and the limited source region. The investigation also implies that obtaining the information on the most probable posture of the exposed worker, as well as the existence of the weekly penetrating radiation such as 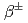 ray as a main source of exposure would be the key for more precise estimation.
ray as a main source of exposure would be the key for more precise estimation.
吉富 寛; 萩原 雅之*; 古渡 意彦; 西野 翔; 佐波 俊哉*; 岩瀬 広*
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1188 - 1195, 2017/11
放射線業務従事者の眼の水晶体や末端部の等価線量については、線量限度を超えていないことを確認するため、適切に評価される必要がある。さらに近年、眼の水晶体に係る線量限度引き下げがICRPにより勧告されたこと、高放射化物等の取り扱いによる末端部被ばくが懸念されることなどから、より妥当な評価が要求されている。これらの部位は体幹部から離れた位置にあることから、場の不均等性によって大きく影響を受けるが、原子力・学術分野で、その不均等性を判断するための仕組みが十分であるとは言えない。本研究では、計算と実験を組み合わせて、不均等性を判断する枠組みを提案した。新たに提案した不均等性を表す指標を数学ファントムを用いたモンテカルロ計算により求め、その妥当性をベンチマーク実験により検証した。さらに、線源条件などのパラメータを変化させたいくつかのケースについて不均等性を調べ、水晶体被ばくにおいて不均等性を判断する上で考慮すべき因子を明らかにした。一連の実験と計算により、本指標の有用性と信頼性を確認することができた。
吉澤 道夫; 辻村 憲雄*
保健物理, 36(1), p.18 - 23, 2001/03
2001年4月からICRP1990年勧告を取り入れた新しい放射線障害防止法令が施行される。この改正法令では外部被ばくモニタリングに関しても、用いる線量の意味の変更等が行われた。これを受けて、外部被ばく線量の測定・評価マニュアルの改定が行われた。本報では、新しいマニュアルに関して、改正法令による主要な変更点である、(1)1cm線量当量等と線量換算係数(場のモニタリング量と個人モニタリング量の区別,換算係数変更の影響)、(2)1cm線量当量等の測定(サーベイメータや個人線量計の対応)、(3)個人モニタリング(3mm線量当量と眼の水晶体の線量評価,体幹部不均等被ばく時の実効線量の算定など)に焦点をあてて、変更の内容とその影響について解説する。また、場のモニタリング、測定器の校正及び線量の記録についても簡単にふれる。
吉富 寛; 古渡 意彦; 萩原 雅之*; 長畔 誠司*; 中村 一*
no journal, ,
ICRPによる眼の水晶体の線量限度低減勧告を受けて、眼の周辺での追加モニタリングやモニタリング量についての議論がなされている。眼の水晶体被ばくの管理には、追加モニタリングを要求すべき作業者をもれなく特定し、確実かつ適切にモニタリングを実施することが必要である。しかし、これまで追加モニタリング実施の意思決定は経験的で曖昧であることが課題であった。IAEA技術文書でも指摘されているように、その意思決定には被ばくの不均等性が重要な因子である。そこで、著者らは、これまで眼の水晶体モニタリングに係る被ばくの不均等性を表す定量化指標(HI)を導入し、事前評価したHIによってモニタリング要否の判断を行う枠組みを提案した。本研究では、加速器施設における作業場において、このHIによる被ばくの不均等性の評価を試みた。経験的に均等被ばく、及び不均等被ばくと考えられる状況に適用し、計算により評価した値とファントム実験により得られた実測値とを比較した。何れのケースにおいても適切にモデリングを行えば、実測値を再現し、被ばくの不均等性を定量的に評価できた。また、放射化した空気による被ばく状況に関しては、経験的には均等被ばく状況と考えられたが、その不均等性は大きく線源の広がりや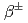 線の影響を考慮する必要があることが分かった。
線の影響を考慮する必要があることが分かった。
辻村 憲雄
no journal, ,
国際放射線防護委員会が「組織反応に関する声明」で勧告した新たな水晶体の等価線量限度の規制への取入れにあたり、「水晶体の放射線防護に関連したガイドライン」の作成準備が勧められている。保健物理学会が主催するシンポジウム「水晶体防護に係るガイドラインを考える」において、ガイドライン作成にあたっての課題や論点整理のため、不均等被ばく時における管理基準の考え方について紹介する。
辻村 憲雄; 横山 須美*
no journal, ,
胸部又は腹部に取り付けた単一の個人線量計では、その着用者の全身の被ばく線量を代表しえない場合がある。このような状況は、一般に「体幹部不均等被ばく」と呼称され、必要に応じて、二個以上の個人線量計を使用し、それら個人線量計の指示値の加重平均から実効線量を算定する個人被ばく管理が現在行われている。しかしながら、そうした管理をどのような条件で行うべきかについては、これまであまり議論がなされていない。海外の事例等を参考にそうした管理の運用基準について解説する。
 線場における不均等被ばく時の水晶体等価線量評価
線場における不均等被ばく時の水晶体等価線量評価山頭 匡治*; 辻村 憲雄; 星 勝也; 青木 克憲; 谷村 嘉彦; 吉富 寛; 横山 須美*
no journal, ,
散乱線を多く含む高 線場においては、遮蔽ベストを着用して作業を行なう場合がある。その場合の作業者の水晶体等価線量は、遮蔽ベストの外側(上腕もしくは胸・頸部)に装着した線量計で評価する。この場合、線量計装着位置の違いによる放射線の入射角度依存性、線量計への後方散乱成分の入射量、そして、作業場の空間分布の違いなどの考慮すべき要素が挙げられる。また、頭部や眼の近傍に線量計を着用することによる負荷についても考えなければならない。そこで、これらの線量評価上の影響要因を明らかにするため、散乱線場の寄与が大きな作業場における作業者の水晶体等価線量を計算によって評価した。
線場においては、遮蔽ベストを着用して作業を行なう場合がある。その場合の作業者の水晶体等価線量は、遮蔽ベストの外側(上腕もしくは胸・頸部)に装着した線量計で評価する。この場合、線量計装着位置の違いによる放射線の入射角度依存性、線量計への後方散乱成分の入射量、そして、作業場の空間分布の違いなどの考慮すべき要素が挙げられる。また、頭部や眼の近傍に線量計を着用することによる負荷についても考えなければならない。そこで、これらの線量評価上の影響要因を明らかにするため、散乱線場の寄与が大きな作業場における作業者の水晶体等価線量を計算によって評価した。
古渡 意彦*; 吉富 寛; 谷村 嘉彦; 栗原 治*
no journal, ,
過去30年間における放射線事故の調査では、25%以上のケースが工業利用における過剰被ばくである。そこで、本研究では、工業用ラジオグラフィーにおいて想定される不均等高線量被ばくについて線量計測上の課題を調査した。これらの事故時においては、装着していた個人線量計の指示値が、被ばく医療などで必要な線量評価において有用な情報となる。しかし、不均等被ばくにおいては、それが直接実効線量や臓器線量のよい推定値を与えるかは議論の余地がある。そこで、数値人体ファントムに対する Cs
Cs  線源の一様照射及び事故時の不均等被ばくを模擬する点線源による照射をモンテカルロ計算でシミュレーションし、胸部に装着した線量計と実効線量、肺の臓器線量の比較を行った。その結果、一様照射では線量計の指示値は保守的な評価をしていたが、点線源の体系では、10倍以上の過小評価をすることが分かった。
線源の一様照射及び事故時の不均等被ばくを模擬する点線源による照射をモンテカルロ計算でシミュレーションし、胸部に装着した線量計と実効線量、肺の臓器線量の比較を行った。その結果、一様照射では線量計の指示値は保守的な評価をしていたが、点線源の体系では、10倍以上の過小評価をすることが分かった。